---
title: Infoveave Query Functions
description: Learn how to use SQL query functions for precise date calculations using business or custom calendars, with support for date granularity.
---
import { Aside, Steps } from '@astrojs/starlight/components';
# Infoveave Query Functions
Infoveave provides a set of query functions for use in SQL queries. These include Infoveave's collection of business and custom calendar date functions. You can embed these functions while writing SQL queries for reports or widgets. The Infoveave SQL functions accept three parameters: Date, Level, and Lag.
* **Date** You can use dates in the form of **@StartDate**, **@EndDate**, or **@CurrentDate**. The valid date format is **"2020-06-19"**.
* **Level** You specify the date granularity using **Years**, **Quarters**, **Months**, **Weeks**, or **Days**. These values are not case-sensitive.
* **Lag** This is usually an integer. The Lag adds or subtracts the specified number of levels to or from the given date.
## Business Dates
Infoveave supports the following functions for using business dates in queries - **@BusinessStart**, **@BusinessEnd**, **@BusinessDays**, **@BusinessDaysExPH**, **@BusinessEndExPH**, and **@BusinessStartExPH**.
### @BusinessStart
This function returns the business start date that is not in the holidays list. This is based on the Date, Level, and Lag that you pass to the function.
Syntax `@BusinessStart(Date, Level, Lag)`
**Examples**
- `Select @BusinessStart("2020-06-19", year, 0) as Date`
This function returns **"2020-01-01"** as the start date of the year. If **"2020-01-01"** is a holiday, then the function returns the next date that is not in the holidays list, such as **"2020-01-02"**.
- `Select @BusinessStart("2020-06-19", year, 1) as Date`
This function adds a Lag value of 1 to the date passed and returns the start date of that year as **"2021-01-01"**.
- `Select @BusinessStart("2020-06-19", year, -1) as Date`
This function subtracts a Lag value of 1 from the date passed and returns the start date of that year as **"2019-01-01"**.
### @BusinessEnd
This function returns the business end date that is not in the holidays list. This is based on the Date, Level, and Lag that you pass to the function.
Syntax `@BusinessEnd(Date, Level, Lag)`
**Examples**
- `Select @BusinessEnd("2020-06-19", year, 0) as Date`
This function returns **"2020-12-31"** as the end date of the year. If **"2020-12-31"** is a holiday, the function returns the previous date that is not in the holidays list, such as **"2020-12-30"**.
- `Select @BusinessEnd("2020-06-19", year, 1) as Date`
This function adds a Lag value of 1 to the date passed and returns the end date of that year as **"2021-12-31"**.
- `Select @BusinessEnd("2020-06-19", year, -1) as Date`
This function subtracts a Lag value of 1 from the date passed and returns the end date of that year as **"2019-12-31"**.
- The business end function also supports an additional Lag **"-0"** which returns the previous date of the current date.
`Select @BusinessEnd("2020-06-19", year, -0) as Date`
This function returns **"2020-06-18"** as the business end date.
### @BusinessDays
This function calculates based on business days. If a business day happens to be a holiday, it is excluded from the count.
Syntax `@BusinessDays(Date, Offset)`
**Examples**
- `Select to_date(@BusinessDays(@CurrentDate, +1), 'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual`
This function returns the next business date after adding 1 business day to the current date. If the next day is a holiday, the function skips it and returns the next valid business day.
- `Select to_date(@BusinessDays(@CurrentDate, 0), 'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual`
This function returns the current date itself if it is a business day. If the current date is a holiday, the function returns the next valid business day.
- `Select to_date(@BusinessDays(@CurrentDate, +2), 'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual`
This function returns the business date after adding 2 business days to the current date. It skips holidays that fall within the range.
### @BusinessDaysExPH
This function returns business days including public holidays that fall on those days.
Syntax `@BusinessDaysExPH(Date, Offset)`
**Examples**
- `Select to_date(@BusinessDaysExPH(@CurrentDate, +1), 'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual`
This function returns the next business date after adding 1 business day to the current date, excluding public holidays.
- `Select to_date(@BusinessDaysExPH(@CurrentDate, 0), 'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual`
This function returns the current date itself if it is a business day. If it is a public holiday, the function returns the next valid business date.
### @BusinessEndExPH
This function considers the end date as a business day even if it falls on a public holiday.
Syntax `@BusinessEndExPH(Date, Level, Lag)`
**Examples**
- `Select @BusinessEndExPH("2024-12-31", year, 0) as Date`
Returns the last day of the current year as a business day, even if **2024-12-31** is a public holiday.
- `Select @BusinessEndExPH("2024-05-01", month, 0) as Date`
Returns **2024-05-31** as a business day, even if it is a public holiday.
- `Select @BusinessEndExPH("2025-01-01", quarter, -1) as Date`
Returns the last business day of the previous quarter, treating the end date as a business day even if it falls on a holiday.
### @BusinessStartExPH
This function considers the start date as a business day even if it falls on a public holiday.
Syntax `@BusinessStartExPH(Date, Level, Lag)`
**Examples**
- `Select to_date(@BusinessStartExPH("2024-01-01", year, 0), 'yyyy-mm-dd') as Date`
Returns the first business day of the current year starting from **2024-01-01**, even if it is a public holiday.
- `Select to_date(@BusinessStartExPH("2024-05-01", month, 0), 'yyyy-mm-dd') as Date`
Returns the first business day of May 2024, treating **2024-05-01** as a business day even if it is a holiday.
- `Select to_date(@BusinessStartExPH("2024-01-01", year, 0), 'yyyy-mm-dd') as Date`
Returns the first business day of the previous quarter, treating the start date **2025-04-01** as a business day even if it falls on a holiday.
## Calendar Dates
Infoveave supports the following functions for using calendar dates in queries - **@CalendarStart** and **@CalendarEnd**.
### @CalendarStart
This function returns the calendar start date that is not in the holidays list. This is based on the Date, Level, and Lag that you pass to the function.
Syntax **@CalendarStart(Date, Level, Lag)**
**Examples**
- `Select @CalendarStart("2020-06-19", year, 0) as Date`
This function returns **"2020-01-01"** as the start date of the year. If **"2020-01-01"** is a holiday, the function returns the next date that is not in the holidays list.
- `Select @CalendarStart("2020-06-19", year, 1) as Date`
This function adds a Lag value of 1 and returns the start of the next year.
- `Select @CalendarStart("2020-06-19", year, -1) as Date`
This function subtracts a Lag value of 1 and returns the start of the previous year.
### @CalendarEnd
This function returns the calendar end date that is not in the holidays list. This is based on the Date, Level, and Lag that you pass to the function.
Syntax **@CalendarEnd(Date, Level, Lag)**
**Examples**
- `Select @CalendarEnd("2020-06-19", year, 0) as Date`
This function returns **"2020-12-31"** as the end date of the year. If it is a holiday, the function returns the previous valid date.
- `Select @CalendarEnd("2020-06-19", year, 1) as Date`
This function adds a Lag value of 1 and returns the end date of the next year.
- `Select @CalendarEnd("2020-06-19", year, -1) as Date`
This function subtracts a Lag value of 1 and returns the end date of the previous year.
- The calendar end function also supports Lag **"-0"**, which returns the previous date of the current date.
`Select @CalendarEnd("2020-06-19", year, -0) as Date`
This function returns **"2020-06-18"** as the calendar end date.
## Others
Infoveave also supports other date functions for use in queries - **@Filters**, **@NonDateFilters**, **@EndDate**, **@StartDate**, **@CurrentDate**.
### @Filters
This function returns the active filter conditions applied to the current context. It automatically includes all selected filter values without the need to reference each one individually.
Whenever you use **@Filters** and click on the **Execute** button, you get a popup to select the date range and add the required filters.
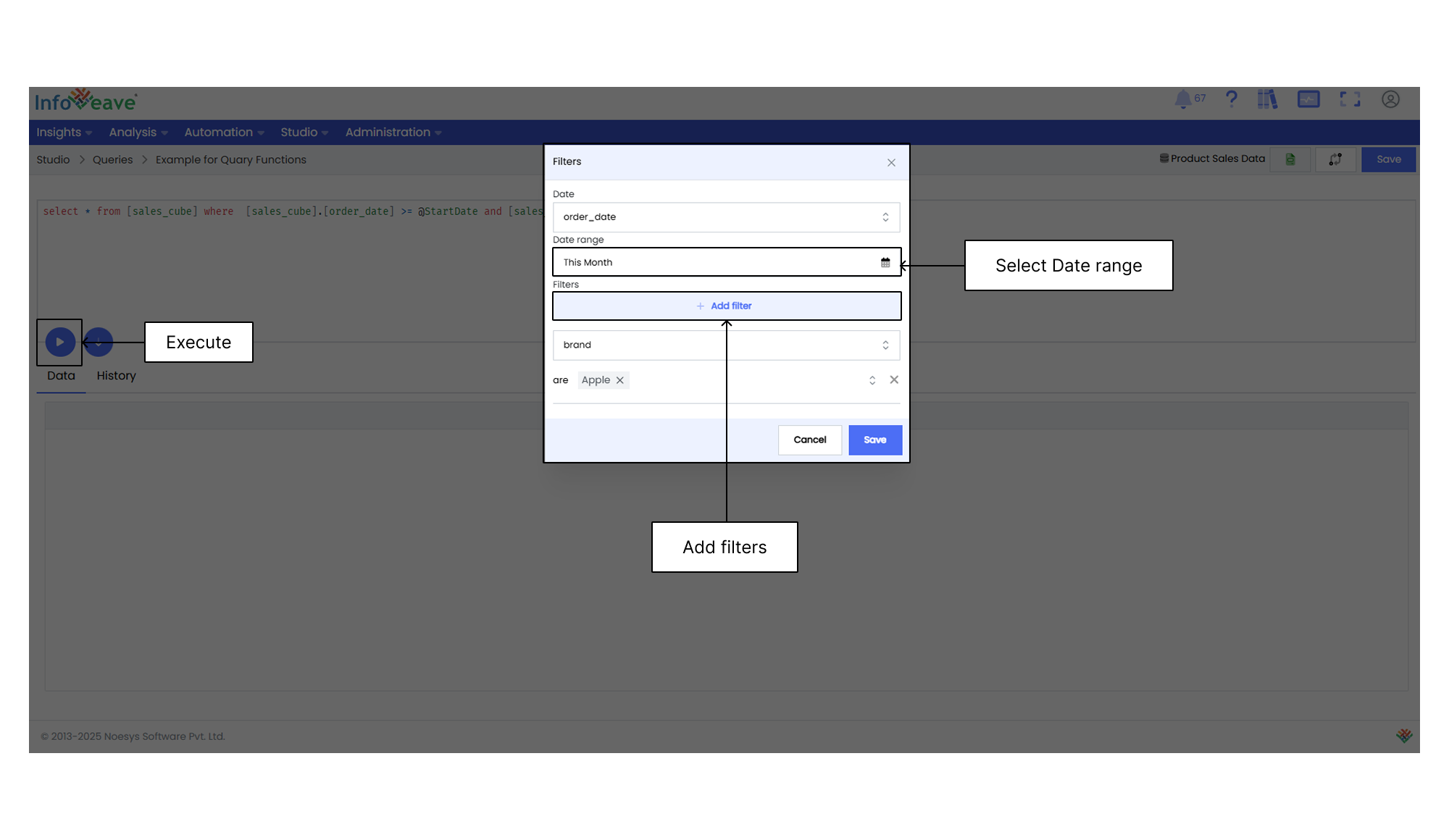
Syntax `@Filters`
**Examples**
- `SELECT * FROM SalesData WHERE 1 = 1 AND @Filters`
Returns all rows from SalesData that match the active filters.
- `SELECT COUNT(*) AS OrderCount FROM Orders WHERE OrderStatus = 'Completed' AND @Filters`
Returns the number of completed orders after applying filters.
- `SELECT CustomerName, SUM(Amount) AS TotalAmount FROM Transactions WHERE PaymentMode = 'Online' AND @Filters GROUP BY CustomerName`
Returns the total amount of online transactions per customer, based on active filters.
### @NonDateFilters
This function returns all records without applying any date filters.
Syntax `@NonDateFilters`
**Examples**
- `SELECT DISTINCT Category FROM [ProductData] WHERE @NonDateFilters`
Returns all product categories without date filters.
- `SELECT DISTINCT CustomerName FROM [CustomerData] WHERE @NonDateFilters`
Returns the list of all customers, ignoring the reporting period.
- `SELECT DISTINCT Region FROM [SalesRegion] WHERE @NonDateFilters`
Returns all available regions in the dataset without any date restrictions.
### @StartDate
This function returns the start date of the selected date range in your filter panel.
Syntax `@StartDate`
**Examples**
- `SELECT * FROM [Orders] WHERE OrderDate >= @StartDate`
Returns all orders placed on or after the start date.
- `SELECT SUM(SalesAmount) FROM [SalesData] WHERE OrderDate >= @StartDate`
Calculates total sales from the start of the period.
- `SELECT * FROM [Employees] WHERE JoinDate >= @StartDate`
Returns employees who joined after the start date.
### @EndDate
This function returns the end date of the selected date range in your filter panel.
Syntax `@EndDate`
**Examples**
- `SELECT * FROM [SalesData] WHERE OrderDate <= @EndDate`
Returns all sales transactions up to the end date.
- `SELECT COUNT(*) FROM [Tickets] WHERE ClosedDate <= @EndDate`
Returns the number of support tickets closed on or before the end date.
- `SELECT * FROM [Invoices] WHERE InvoiceDate <= @EndDate`
Returns all invoices generated on or before the end date.
### @CurrentDate
This function returns the current system date in the format "YYYY-MM-DD".
Syntax `@CurrentDate`
**Examples**
- `SELECT * FROM Sales WHERE SaleDate = @CurrentDate;`
Get all sales made today.
- `SELECT * FROM Users WHERE SignupDate = @CurrentDate;`
Find all users who signed up today.
- `SELECT * FROM InventoryLogs WHERE UpdatedOn = @CurrentDate;`
Check inventory updates done today.